How Do I Calculate Self-Employed Income?
Being self-employed comes with its own set of perks and responsibilities, and one crucial aspect is calculating your income accurately. Unlike traditional employment where a regular paycheck is received, self-employed individuals need to determine their income based on various factors. In this article, we will walk you through the essential steps on how to calculate self-employed income, helping you gain a clear understanding of your financial situation.
Record And Organize Income Sources:
The first step in calculating self-employed income is to identify and gather all your income sources. As a self-employed individual, your earnings can come from various avenues such as freelance work, consulting, sales of products or services, rental income, and more. Keep detailed records of all transactions and organize them systematically.
Gross Income Calculation:
To determine your gross self-employed income, sum up all the earnings from your different income sources. This should include all the revenue generated before deducting any expenses or taxes. It is essential to have accurate and up-to-date records to ensure your calculations are precise.
Business Expenses Deduction:
One advantage of being self-employed is the ability to deduct legitimate business expenses from your gross income. These expenses include costs incurred for running your business, such as office rent, utilities, equipment, supplies, marketing expenses, professional services fees, and travel expenses directly related to business activities. Keep all receipts and relevant documentation as proof for potential audits.
Calculate Net Income:
To calculate your net self-employed income, subtract your total business expenses from your gross income. Net income reflects the actual amount you earn after deducting expenses. It is crucial to differentiate between personal and business expenses to ensure accurate calculations.
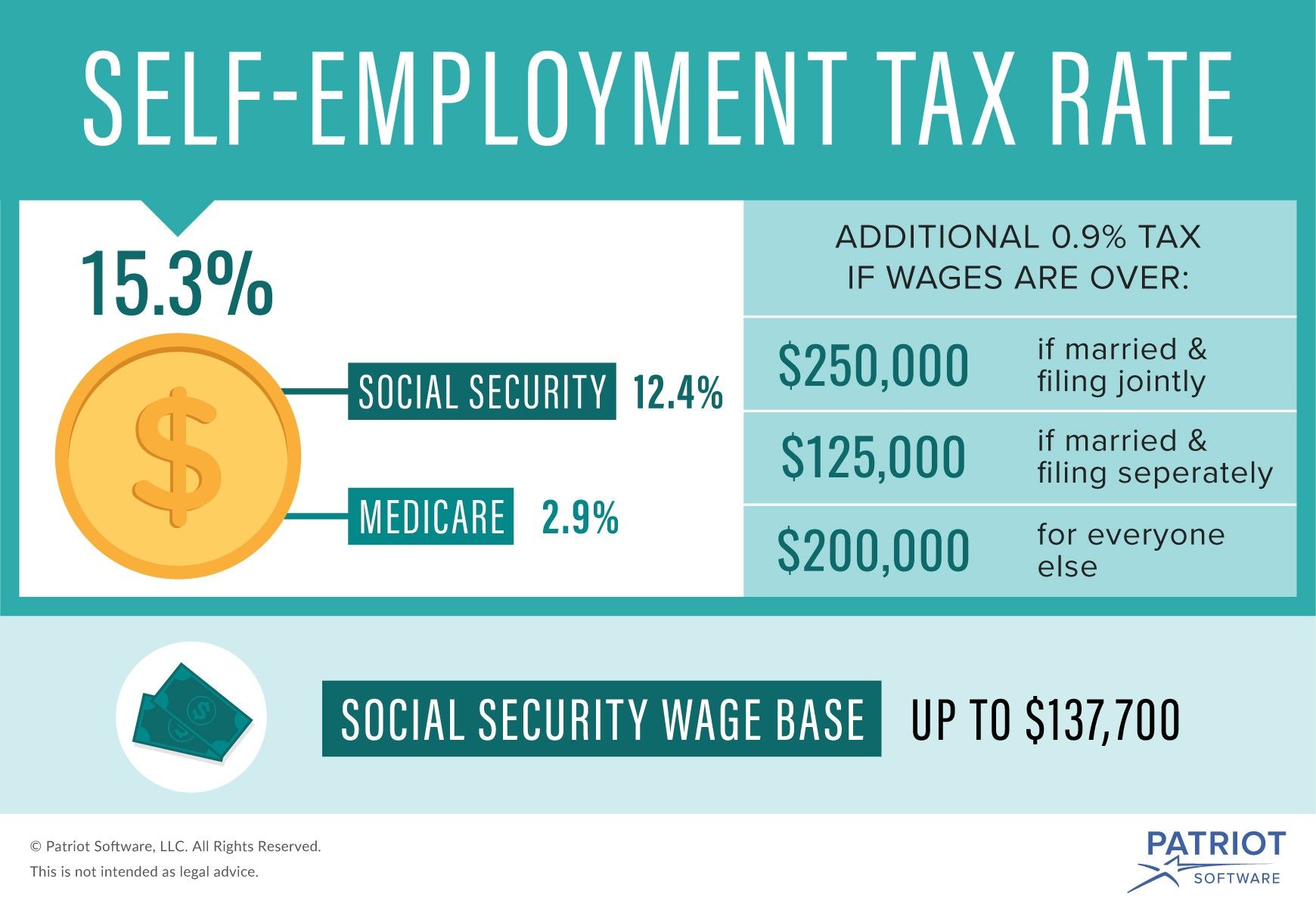
Self-Employment Tax:
Self-employed individuals are responsible for paying both the employer and employee portions of Social Security and Medicare taxes. These are commonly referred to as self-employment taxes. The self-employment tax rate is typically higher than the tax rate for regular employees. It is essential to factor in this additional tax obligation when calculating your self-employed income. To simplify the process of calculating self-employment taxes accurately, a self-employment income calculator is an invaluable tool. This calculator takes into account various factors such as income, business expenses, and deductions to determine the self-employment tax liability.
Estimated Tax Payments:
Unlike employees who have taxes withheld from their paychecks, self-employed individuals must make estimated tax payments to the IRS throughout the year. Based on your projected income, you need to estimate your tax liability and make quarterly payments to avoid penalties and interest charges.
Consult A Professional:
Calculating self-employed income can be complex, especially if you have multiple income streams or face unique circumstances. In such cases, it is highly recommended to seek guidance from a qualified tax professional or accountant. They can help ensure accurate calculations, maximize deductions, and provide valuable advice on managing your finances. In conjunction with seeking professional advice, utilizing a consultant tax calculator can enhance your tax planning efforts. A consultant tax calculator is a specialized tool designed to assist individuals in the consulting industry in accurately estimating their tax liabilities. It takes into account factors such as income, business expenses, deductions, and industry-specific regulations to provide an accurate projection of tax obligations.
Keep Track Of Business Mileage:
If you use your vehicle for business purposes, it’s crucial to track your mileage accurately. The IRS allows self-employed individuals to deduct business-related mileage expenses. Keep a log of the dates, destinations, and purpose of each trip to substantiate your deductions. You can either use a mileage tracking app or maintain a physical record.
Separate Personal And Business Finances:
Maintaining separate bank accounts and credit cards for your personal and business finances is essential. This practice not only simplifies income calculation but also helps in tracking business expenses accurately. It’s recommended to have a dedicated business account to deposit income and pay business-related expenses. This separation of finances provides a clear picture of your self-employed income and ensures compliance with tax regulations.
Consider Depreciation And Amortization:
If your self-employment involves the use of assets like equipment, vehicles, or computers, you may be eligible to deduct depreciation or amortization expenses. These deductions account for the wear and tear of your business assets over time. Consulting with a tax professional will help you understand the applicable rules and maximize your deductions.
Stay Informed About Tax Laws And Regulations:
Tax laws and regulations are subject to change, so it’s crucial to stay informed about any updates that may affect your self-employed income calculations. Subscribe to reliable tax publications or consult a tax professional to ensure you are aware of any new deductions, credits, or changes in tax rates that could impact your financial situation.
Conclusion:
Calculating self-employed income is an essential task that every self-employed individual must undertake. By accurately tracking your income sources, deducting legitimate business expenses, and factoring in self-employment taxes, you can gain a clear understanding of your financial situation. Maintaining organized records, making timely estimated tax payments, and seeking professional assistance when needed will help you navigate the intricacies of self-employed income calculation. With this knowledge, you can make informed decisions, plan for the future, and ensure your business thrives financially.
ALSO READ: Ways to calculate life insurance needs

Post Comment